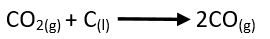ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
Figure
|
Source of Figure
|
Figure 5
|
http://sciencepark.etacude.com
|
Extraction of Iron:
Ore:
Iron is
found in the earth’s crust in the form of its ores; hematite, (Fe2O3) and magnetite, (Fe3O4). Iron is largely extracted from hematite, as it contains the largest percentage composition of
Iron.
Extraction technique:
- The ore is thoroughly washed with water to remove impurities like rocks and sand.
- The purified ore is roasted on heat in the presence of oxygen to oxidize any carbon impurity to carbon dioxide.
- The roasted ore along with limestone and coke is fed into the blast furnace for reduction to iron.
- Figure 5: Blast furnace
- A regular blast furnace is 32m in height and 1m in width
- The blast furnace is called the blast furnace due to the blasts of air which are pumped from the bottom of the furnace to ensure complete reduction.
- The temperature at the bottom of the furnace is maintained at 1900°C to melt the ore. The temperature decreases slightly towards the top of the furnace with the coldest end being at 1000°C.
- The raw material; ore, coke and limestone are added from the top of the furnace.
- Hematite, Fe2O3, reacts with coke, C, to form Iron oxide, FeO and Carbon monoxide, CO.
- Calcium carbonate, CaCO3, added as a flux decomposes to calcium oxide, CaO, and carbon dioxide, CO2.
- This carbon dioxide, rises to the top of the furnace and reacts with the incoming carbon to form carbon monoxide.
- This carbon monoxide in the furnace reduces the iron oxide to iron.
- The released carbon dioxide gas escapes via the gas outlets on the top of the furnace.
- The calcium oxide formed reacts with the sand particles to form slag.
- This slag is less dense than molten iron and floats on top of it and can be extracted from the furnace’s top outlet. Slag is solidified and used in the construction of roads.
- Molten iron is extracted from bottom outlet. It is casted in moulds to solidify. This iron is called cast iron.